Page 48 - My FlipBook
P. 48
58 ANA TOM Y.
sphenoid, leaving a portion unoccupied by bone. This unoccupied
portion is called the middle lacerated foramen, and is filled up ^vith
cartilage in the recent state. It has three surfaces : two (the anterior
and posterior) are situated within the brain-case; the other, the inferior,
on the outside.
The Anterior Surface looks forward and upward, marking in the base
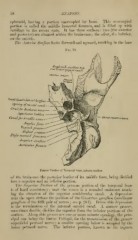
Fig. 19.
C'tvahfirlu.^tachan tube
LEVATOR PAL
Rough Quadrilateral
SnrJ'a^e
^r^-^iny of carotid en.,nd
Ca7ialfor Iacol.,on\ nerve
^\ijur^i,ctus Ciir/ilecc
STVLO-PHARyNGEus
Canal for Avnold:, mrve
Ji'ffiilar /hs-sa
^'tt/Lnal jyrijceas
jSffyloid process-
Stylo- mastoid foramen
Jii^xUor Surface
Auricular fissure
Petrous Portiou of Temporal Bone, inferior surface.
of the brain-ca.se the posterior border of its middle fossa, being divided
into a superior and an inferior })ortion.
The Sxpcrior Portion of the ])ctrous portion of the temporal bone
is of hard consistency; near the centre is a rounded eminence mark-
ing the situation of the snj)erior semicircular canal. A depression
near the apex defines the position of the Gasserian ganglion (semilunar
ganglion of the fifth ])air of nerves; see p. 284). Below this depression
is the termination of the internal carotid canal. A narrow groove,
sometimes doul)lc, divides the superior from the inferior portions of the
surface. Along this groove arc one or more minute openings, the prin-
cipal one being the hiatus Fallopii, for the transmission of the greater
superficial petrosal nerve ; a smaller opening below is occupied by the
lesser petrosal nerve. Tlie inferior portion, known as the tegmen