Page 293 - My FlipBook
P. 293
—
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. 303
parotid gland, the chorda tympani, tensor tympani, palato-Eustachian
muscles, and the mucous membrane of the middle ear.
The Submaxillary Ganglion.
The submaxillarv or lingual ganglion is situated above the deep
portion of the submaxillary muco-salivary gland, close to the outer
portion of the hyo-glossus muscle. It varies in shape and size, usually
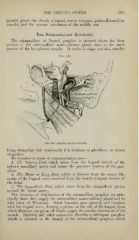
Fig. 147.
The otic Ganglion and its Branches.
being triangular, but occasionally it is fusiform or plexiform, or absent
altogether.
Its branches or roots of communication are
1. The Sensori/ Boot, which arises from the lingual branch of the
inferior maxillary nerve and enters the posterior portion of the gan-
glion.
2. The Motor or Long Boot, which is formed from the motor fila-
ments of the lingual nerve received from the chorda tympani branch of
the facial.
3. The Si/mpathetic Boot, which arises from the sympathetic plexus
around the facial artery.
The branches of distribution of the submaxillary ganglion are prin-
cipally those that supply the submaxillary muco-salivary gland and its
duct (duct of Wharton). Other branches pass upward, and interlace
with the lingual nerve, forming a plexus on the side of the tongue, from
which filaments are given off which supply the mucous membrane of the
mouth. Baldwin and other anatomists describe a sublingual ganglion
which is situated on the branch of the submaxillary ganglion which
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. 303
parotid gland, the chorda tympani, tensor tympani, palato-Eustachian
muscles, and the mucous membrane of the middle ear.
The Submaxillary Ganglion.
The submaxillarv or lingual ganglion is situated above the deep
portion of the submaxillary muco-salivary gland, close to the outer
portion of the hyo-glossus muscle. It varies in shape and size, usually
Fig. 147.
The otic Ganglion and its Branches.
being triangular, but occasionally it is fusiform or plexiform, or absent
altogether.
Its branches or roots of communication are
1. The Sensori/ Boot, which arises from the lingual branch of the
inferior maxillary nerve and enters the posterior portion of the gan-
glion.
2. The Motor or Long Boot, which is formed from the motor fila-
ments of the lingual nerve received from the chorda tympani branch of
the facial.
3. The Si/mpathetic Boot, which arises from the sympathetic plexus
around the facial artery.
The branches of distribution of the submaxillary ganglion are prin-
cipally those that supply the submaxillary muco-salivary gland and its
duct (duct of Wharton). Other branches pass upward, and interlace
with the lingual nerve, forming a plexus on the side of the tongue, from
which filaments are given off which supply the mucous membrane of the
mouth. Baldwin and other anatomists describe a sublingual ganglion
which is situated on the branch of the submaxillary ganglion which