Page 296 - My FlipBook
P. 296
306 ANATOMY.
n , • -1 f Anricnlar.
Posterior aunciuar, -, , • »
, i
(. (_)cfipital.
'
Stylo-livoid.
Digastric.
Stylo-glossal.
After escaping from the stylo-mast oid
Temporal.
foramen, I
Temporo-facial, < Malar.
( Intraorbital.
f Buccal.
Cervico-facial, < fSupramaxillary.
( Cervical.
The Geniculate Ganglion (intumescentia ganglioformis) is a reddish
enlargement on the foremost part of the facial nerve, which contains
numerous nerve-cells. It is situ-
Fifi. 149.
ated on the curve as the nerve
turns from the horizontal to the per-
pendicular direction in the aqueduct
of Fallopius. It does not receive
all the fibres of the facial nerve, but
receives the terminal ends of the nerve
of Wrisberg. The nerves arising
from this p;ano;lion are six in num-
ber, the names of which will be found
in the ])receding table.
The Great Superficial Petrosal Nerve
(Fig. 149) arises from the geniculate
ganglion of the seventh nerve, and is
the largest of the ganglionic branc-hes.
It passes forward through the hiatus
Fallopii on the superior portion of
the anterior surface of the petrous
portion of the temporal bone, from
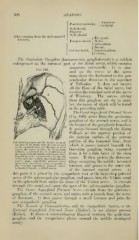
'ihis drawing represents the Middle Fossa of
the Uase of the Skull, with the petrous part which it passes inward beneath the
of the temporal bone cut through so as to
expose the nerves joiniug the facial (from Gusserian ganglion, being separated
Kidder): '/, external ear; h, middle fossa of
the skull, witli the middle meningeal artery from it by a thin layer of the dura
branching on it ; 1, facial nerve by the side mater. It then pierces the fibro-car-
of the auditory; 2, large superficial petrosal
nerve; small superficial petrosal nerve tilage occupying the middle lacerated
lying over the tensor tynipani inuscle; 4,
the external superficial petrosal nerve; foramen, and passes to the outer side
5, chorda tynipani ; S, eighth nerve.
of the internal carotid artery. At
this point it is joined by the symjjathetic root or the large deep petrosal
nerve of the spiieno-palatine ganglion, and passes into the Vidian canal
in the s]:>henoid bone under the name of the Vidian nerve. It extends
til rough this canal, and enters the apex of the spheno-palatine ganglion.
The Le.sf
of Jacobson. It then passes through a small foramen and joins the
otic sympathetic ganglion.
The Branch of Comrmoi leaf ion n-if/i flic Si/mpafJietic Si/stem, or the
External Superficial Petrosal Nerve (Bidder), is not always jiresent
(Ruber). It forms a connnunicating filament between the geniculate
ganglion and the sympathetic plexus around the middle meningeal
artery.