Page 290 - My FlipBook
P. 290
300 ANATOMY.
it, and receive no influence from it. These fibres fi^rm tiie palatine
nerves.
2. The Motor Root, which is quite long, and arises from the facial
nerve or the large superficial petrosal nerve at the geniculate ganglion
(intumescentia gangliaformis) within the aqueduct of Fallopius. From
this point it passes forward through the hiatus Fallopii on the anterior
surface of the petrous portion of the temporal bone, then inward beneath
the Gasserian ganglion, being separated from it by a thin layer of dura
mater. It then pierces the fibro-cartilage occupying the middle lace-
rated foramen, and passes to the outer side of the internal carotid artery.
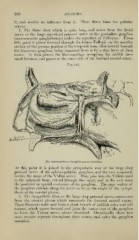
Fig. 146.
The Spheno-palatine Ganglion and its Branches.
At this point it is joined by the sympathetic root or the large deep
petrosal nerve of the spheno-palatine ganglion, and the two conjointly
receive the name of the Vidian nerve. They pass into the Vidian canal
in the sphenoid bone, extend through this canal, and at the exit enter
the posterior or apicial extremity of the ganglion. The gray matter of
the ganglion extends along the nerve as far as the origin of the sympa-
thetic at the carotid plexus.
3. The St/mpathcfic Boot, or the large deep petrosal nerve, commences
from the carotid plexus which surrounds the internal carotid artery.
These filaments unite and form a short branch of reddish color and soft
texture, which passes forward and joins the motor root of the ganglion
to form the Vidian nerve, above described. Occasionally these two
roots remain separate throughout their course, and enter the ganglion
ununited.