Page 574 - My FlipBook
P. 574
584 DENTAL EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY
delicate tissues of the brain-substance, which is being ditFerentiated
even at this early period.
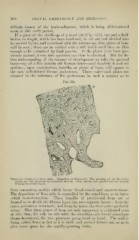
If a piece of the skull-cap of a ftetal cat (Fig. 323), one and a half
inches in length, which lias been hardened, be cut out and divided into
its several layers, and examined with the microscope, thin plates of bone
will be seen; these can be rubbed with a stiff brush until they are thin
enough to be examined by high powers. If the })lates have l)een pre-
viously stained, a very nice specimen can thus be obtained. But for the
best understanding of the manner of development we take the parietal
bone—say of a five months old human foetus—and decalcify it and cut
sections; upon examination, lamellae, or plates of lione, will appear in
the now well-defined fibrous periosteum. These eml)ryonal jilates are
situated in the substance of the periosteum in such a manner as to
Fig. 324.
m'^'-^(^^
Transverse Section of a Bone (ulna). (Magnified 20 diameters.) The openings of the Haversi.in
canals are .seen encircled by concentric lamellae. Other lamelke run parallel with the surface,
forming the cortical layer.
form connecting cavities which locate blood-vessels and marrow -ti.-;sue.
The deposition of lime salts is controlled l)y the osteoblasts, as in inter-
stitial bone-formation. These lamellae of provisional bone are so
located as to divide the fibrous layer into two sejiarate layers : from the
onter, periosteum is formed ; and from the inner, the (ha-a mater probably
arises. That the.'^e ])lates of bone are only temporary is evidenced even
at this time, for side by side with the osteol)lasts are found o.steoclasts
(bone-de.stroyers), the two proces.-^es going hand in hand. The wall is
being taken down as fast as it is built and carried farther out, so as to
give more space for the rapidly-growing brain.