Page 437 - My FlipBook
P. 437
TEETH OF THE VERTEBRATA. 447
not being represented in the deciduous dentine. The formula, wlien they
are normally developed, is I. C. \, M. |=^ = 20, the premolars or
f,
bicuspids being confined to the permanent set. A marked point of dis-
similarity, as compared with their successors, is in the termination of the
enamel on the neck of the tooth. In the permanent teeth the gradual
completion of the enamel on the border of the cement marks but indis-
tinctly the point of union of these two structures, while at the base of
the deciduous crown the terminatino- enamel on the buccal and labial
surfaces is recognized by a ridge or well-defined border which unmis-
takably marks its limitation and develops a well-constricted neck. This
ditfereuce is often of importance in deciding as to whether a tooth in
question belongs to the deciduous or permanent series. These teeth,
from the fact that their crowns are largely calcified before birth, are
much less liable to vices in conformation than their successors, but from
deficient nutrition, want of use, and neglect not unfrequently become an
easy prey to the ravages of deutal caries. In common with a large class
of the order to which man is closely allied, the difference in number
betw^een the deciduous and permanent set is twelve, the additional
teeth being without predecessors.
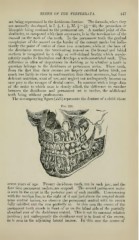
The accompanying figure (226) represents the denture of a child about
Fig. 226.
seven years of age. Twenty deciduous teeth, ten in each jaw, and the
four first permanent molars, are erupted. The second permanent molar
is seen in the crypt in the posterior part of each maxilla. Commencing
with the median line, to the right of it and just above the erupted decid-
uous central incisor, we observe the permanent central with its crown
fully calcified and the root partially so. In this case the crown of the
permanent tooth stands in front of or on the labial side of the partially
absorbed root of the deciduous central. This is not its constant relative
position ; not unfrequently the deciduous root is in front of the crown,
as is seen in the adjoining lateral incisor. In this case the crown of