Page 272 - My FlipBook
P. 272
282 ANATOMY.
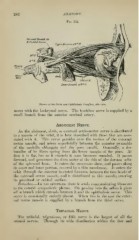
Fig. 142.
IntemaX CarvtiJ, As.
A Cairottd Plea:uj
Boot
Nerves of the Orbit and Ophthalmic Ganglion, side view.
raoses with the lachrymal nerve. The trochlear nerve is supplied by a
small branch from the anterior cerebral artery.
Abducent Nerve.
As the abducent, sixth, or external oculo-motor nerve is distributed
to a muscle of the orbit, it is here described with those that are asso-
ciated with it. This nerve presides over the motion of the external
rectus muscle, and arises superficially between the anterior pyramids
of the medulla oblongata and the pons varolii. Generally, a few
bundles of its fibres spring from the lower margin of the pons. At
first it is flat, but as it extends it soon l)ecomes rounded. It passes
forward, and penetrates the dura mater at the side of the dorsum sellse
of the sphenoid bone. It enters the cavernous sinus, and passes along
its outer and inner portion, covered by a thin membrane. It enters the
orbit througli the anterior lacerated foramen, between the two heads of
the external rectus muscle, and is distributed to this muscle, entering
its proximal or orbital surface.
Branches.— In the cavernous sinus it sends communicating filaments
to the carotid .sympathetic ])lexus. On ]>asi^ing into the orbits it gives
off a branch which extends between it :nid the ()])hthalmic nerve. This
nerve is occasionally entirely absent. A\'lien this is the case the exter-
nal rectus nm.scle is su])})lied by a branch from the third nerve.
Trifacial Nerve.
The trifacial, trigeminus, or fifth nerve is the largest of all the
cranial nerves. Through its wide distribution within the face and