Page 268 - My FlipBook
P. 268
278 ANA TOMY.
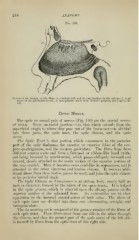
Fig. 139.
Nerves of the Septum of the Nose: 1, olfactory bulb and its ramifications in the septum; 2, nasal
nerve of the ophthalmic trunk 3, naso-palatine nerve from Meckel's ganglion (too large in the
;
cut).
Optic Nerve.
The optic or second pair of nerves (l^'ig. 140) are the special nerves
of vision. Their encranial portion—viz. that which extends from the
superficial origin to where they pass out of the brain-case—is divided
into three parts, the optic tract, the optic chiasm, and the optic
nerve.
The Optic, Tract is that portion which commences in the po.sterior
part of the optic tlialamus, the anterior or superior lobes of the cor-
])ora quadrigemina, and the corpora geniculata. The fibres from these
different sources unite and form a. flattened or ribbon-like band (with-
out being invested by neurilemma), which passes obliquely forward and
inward, clo.sely attached to the under surface of the superior portion of
the cms cerebri. Here it becomes more cord-like in appearance, and is
attached to the tuber cinereum and lamina cinerea. It receives addi-
tional fil)res from these bodies, j^as.ses forward, and joins the optic chiasm
at its posterior lateral angle.
The Optic Chiasm or Commissure is an oblong body, nearly half an
inch in diameter, formed by the union of the optic tracts. It is lodged
in the optic groove, which is situated u})on the olivary process on the
superior surface of the sphenoid bone. Its extremities are in close
apjiosition to the internal carotid artery of both sides. The fibres of
each o])tic tra(!t are divided into three sets—decussating, straight, and
intrageniculate.
Tiie decu.ssating set is compo.sed of the greater number of the fibres of
each o])tic tract. TIum' fibres cross from one side to the other through
the chiasm, and thus tiie greater part of the optic nerve of the left side
is formed by fibres from the optic tract of the right side.