Page 26 - My FlipBook
P. 26
36 ANATOMY
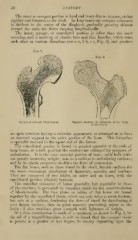
The outer or compact portion is hard and ivory-hke in texture, giving
rigidity and firmness to the shaft. In long bones the compact substance
is thickest in the centre of the diaphysis, gradually growing thinner
toward the ends, the fibres running longitudinally.
The inner, spongy, or cancellated portion is softer than the outer
covering, and is made up of slender bars and thin lamellae, which cross
each other in various directions (see a a, b b, e c, Fig. 2), and produce
Fig. 1.
Fig. 2.
Section of a Sound Adult Femur. Diagram showing the Structure of tlie Neck
of the lemur.
an open structure having a reticular appearance, so arranged as to form
an internal support to the outer portion of the bone. This formation
is specially marked in the upper end of the femur.
The cancellated portion is found in greatest quantity at the ends of
long l)oncs, at ^vhicli position the surfaces are enlarged for purposes of
articulation. It is the more vascular portion of bone; adds bulk with-
out greatly increasing weight; acts as a cushion to articulating surfaces;
and by its elastic projierties modifies the force of concussion.
The flat bones, such as those found in the skull, furnish surfaces for
the more convenient attachment of ligaments, nuiscles, and tendons.
They are comjioscd of two tables, an outer and an inner, with the
cancellated j^ortion (diploe) between.
The cancellar substance of bones generally, but especially in those
of the cranium, is pervaded liy irregular canals for the accommodation
of })lood-vosscls. The two ])Iates or tables of flat bones are bound
together by the cancellated tissue, wliich not only helps to resist fracture,
but acts as a cushion, deadening the force of shock by distributing it
over larger surfaces, thus in great measure preventing injury to the
brain : it also combines great strength M-ith lightness of weight.
If a close examination is made of a specimen, as shown in Fig. 1, by
the aid of a magnifving-glass, it will be found that the compact tissue
is porous in a greater or less degree, its density depending u])on the
The outer or compact portion is hard and ivory-hke in texture, giving
rigidity and firmness to the shaft. In long bones the compact substance
is thickest in the centre of the diaphysis, gradually growing thinner
toward the ends, the fibres running longitudinally.
The inner, spongy, or cancellated portion is softer than the outer
covering, and is made up of slender bars and thin lamellae, which cross
each other in various directions (see a a, b b, e c, Fig. 2), and produce
Fig. 1.
Fig. 2.
Section of a Sound Adult Femur. Diagram showing the Structure of tlie Neck
of the lemur.
an open structure having a reticular appearance, so arranged as to form
an internal support to the outer portion of the bone. This formation
is specially marked in the upper end of the femur.
The cancellated portion is found in greatest quantity at the ends of
long l)oncs, at ^vhicli position the surfaces are enlarged for purposes of
articulation. It is the more vascular portion of bone; adds bulk with-
out greatly increasing weight; acts as a cushion to articulating surfaces;
and by its elastic projierties modifies the force of concussion.
The flat bones, such as those found in the skull, furnish surfaces for
the more convenient attachment of ligaments, nuiscles, and tendons.
They are comjioscd of two tables, an outer and an inner, with the
cancellated j^ortion (diploe) between.
The cancellar substance of bones generally, but especially in those
of the cranium, is pervaded liy irregular canals for the accommodation
of })lood-vosscls. The two ])Iates or tables of flat bones are bound
together by the cancellated tissue, wliich not only helps to resist fracture,
but acts as a cushion, deadening the force of shock by distributing it
over larger surfaces, thus in great measure preventing injury to the
brain : it also combines great strength M-ith lightness of weight.
If a close examination is made of a specimen, as shown in Fig. 1, by
the aid of a magnifving-glass, it will be found that the compact tissue
is porous in a greater or less degree, its density depending u])on the