Page 228 - My FlipBook
P. 228
238 ANATOMY
artery passes through the upper wall of the cavernous sinus. Just
above this point the optic nerve passes to the inside of the artery, while
tlie third nerve passes externally. Near the anterior clinoid process this
portion of the artery gives off its first large branch, the ophthalmic,
while near the iissure of Sylvius it gives off the lateral (posterior) com-
municating artery of the circle of Willis. Above this point it finally
divides into the middle and anterior cerebral arteries.
The branches of this portion of the artery are the ophthalmic, the
anterior, and the middle cerebral.
The Ophthalmic Artery (Fig. Ill) is about 2 mm. (y^. inch) in cali-
bre. It is the first large branch of the internal carotid, arising from
that artery immediately after it passes through the dura mater, at the
last curve of the sigmoid flexure, just internal to the anterior clinoid
process. From this point it passes forward and a little outward over
the anterior portion of the cavernous sinus, through the optic foramen
into the cavity of the orbit, passing below and to the outer side of the
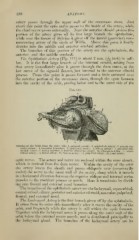
Fig. 111.
Arteries of the Orbit, from the outer side: 1, internal carotid ; 2, ojjhthahiiic arterv ; 3, arteria cen-
tralis retinie; 4, muscular branches; 5, lachrymal artery; (i, ciliMry artery ; "7, posterior eth-
moidal artery; S, rectus inferior; 9. anterior ethmoidal arterv; 10, obi iqu us" inferior; 11, supra-
orbital artery 12, facial iirtery l:i, frontal artery
; ; ; 14, palpebral artery ; 15, nasal artery.
optic nerve. The artery and nerve are enclosed within the same sheath,
which is derived from the dura mater. Within the cavity of the orbit
the artery leaves the sheath and pa.sses obliquely over" (occasionally
under) the nerve to the inner wall of the cavity, along which it travels
in a horizontal direction between the superior oblique and internal rectus
muscles to tlie trochlear ]>rocess or notch. Here it terminates by divid-
ing into frontal and external nasal branches.
The bran('he.s of the o})hthalmic artery are the lachrymal, supraorbital,
central retinal, ciliary, posterior and anterior ethmoid, muscular, palpebral,
frontal, and external nasal.
The Lnrhri/mal Artery is the first branch given off by the ophthalmic.
It arises from its outer side immediately after it enters the cavity of the
orbit, and frequently while the artery is still within the optic foramen.
Together with the lachrymal nerve it pas.ses along the outer wall of the
orbit below the external rectus muscle, and is distributed principally to
the lachrymal gland. The branches of the lachrymal artery are its