Page 674 - My FlipBook
P. 674
;
«72 MANAGEMENT OF THE DECIDUOUS TEETH.
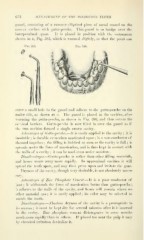
guard, consisting of a concave elliptical j)iece of metal coated on the
convex surface with gutta-percha. This guard is to bridge over the
interproximal space. It is placed in position with the instrument
shown in B, Fig. 595, which is warmed slightly, so that the point can
Fig. 595. Fig. 596.
-enter a small hole in the guard and adhere to the gutta-percha on the
under side, as shown at c. The guard is placed in the cavities, after
warming the gutta-percha, as shown in Fig. 596, and thus covers the
cervical borders. Gutta-percha is now filled in over the guard as if
the two cavities formed a single crown cavity.
Advantages of Gutta-percha.—It is easily applied to the cavity; it is
insoluble ; is durable even when masticated upon ; is a non-conductor of
thermal impulses ; the filling is finished as soon as the cavity is full ; it
spreads under the force of mastication, and is thus kept in contact with
the walls of a cavity ; it can be used even under moisture.
Disadvantages.—Gutta-percha is softer than other filling materials,
and hence wears away more rapidly. In approximal cavities it will
spread the teeth apart, and may then press upon and irritate the gum.
Dryness of the cavity, though very desirable, is not absolutely neces-
sary.
Advantages of Zinc Phosphate Cement.—It is a poor conductor of
it withstands the force of mastication better than gutta-percha
heat ;
it adheres to the walls of the cavity, and hence will remain where no
other material can ; it is easily applied ; its color may be selected to
match the tooth.
Disadvantages.—Absolute dryness of the cavity is a prerequisite to
its success ; it must be kept dry for several minutes after it is inserted
in the cavity. Zinc phosphate cement disintegrates in some mouths
much more rapidly than in others. If placed too near the pulp it may
by chemical irritation devitalize it.
«72 MANAGEMENT OF THE DECIDUOUS TEETH.
guard, consisting of a concave elliptical j)iece of metal coated on the
convex surface with gutta-percha. This guard is to bridge over the
interproximal space. It is placed in position with the instrument
shown in B, Fig. 595, which is warmed slightly, so that the point can
Fig. 595. Fig. 596.
-enter a small hole in the guard and adhere to the gutta-percha on the
under side, as shown at c. The guard is placed in the cavities, after
warming the gutta-percha, as shown in Fig. 596, and thus covers the
cervical borders. Gutta-percha is now filled in over the guard as if
the two cavities formed a single crown cavity.
Advantages of Gutta-percha.—It is easily applied to the cavity; it is
insoluble ; is durable even when masticated upon ; is a non-conductor of
thermal impulses ; the filling is finished as soon as the cavity is full ; it
spreads under the force of mastication, and is thus kept in contact with
the walls of a cavity ; it can be used even under moisture.
Disadvantages.—Gutta-percha is softer than other filling materials,
and hence wears away more rapidly. In approximal cavities it will
spread the teeth apart, and may then press upon and irritate the gum.
Dryness of the cavity, though very desirable, is not absolutely neces-
sary.
Advantages of Zinc Phosphate Cement.—It is a poor conductor of
it withstands the force of mastication better than gutta-percha
heat ;
it adheres to the walls of the cavity, and hence will remain where no
other material can ; it is easily applied ; its color may be selected to
match the tooth.
Disadvantages.—Absolute dryness of the cavity is a prerequisite to
its success ; it must be kept dry for several minutes after it is inserted
in the cavity. Zinc phosphate cement disintegrates in some mouths
much more rapidly than in others. If placed too near the pulp it may
by chemical irritation devitalize it.