Page 104 - My FlipBook
P. 104
114 ANA TOMY
maxillary, not being in direct connection with the joint, will be
described as accessory ligaments to the articulation (Fig. 58).
The Capsular Ligaments of the temporo-maxillary articulation is an
exceedingly loose fibrous bag. It is thin in front and on the inner side,
being thick and strong behind and on the outer side. It is attached
above to the articulating circumference of the glenoid fossa, and below
it encircles the neck of the condyle of the inferior maxilla. The most
superficial fibres of this ligament extend downward and backward from
the outer surface and tubenslc at the anterior root of the zygoma to the
outer surface and posterior border of the neck of the inferior maxilla.
This portion is generally spoken of as the external lateral ligament of
the articulation.
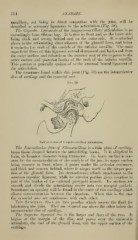
The structures found within this joint (Fig. 59) are the interarticular
disc of cartilage and the synovial sacs.
Ym. 59.
Vertical Sectiou of Temporo-maxillary Articulation.
The Interarticular Dhic of Fibro-cartilage is a thin jilate of cartilag-
inous tissue situated between the articulating bones. It is elliptical in
form, its broadest diameter being transverse. Its lower surface is con-
cave for the accommodation of the condyle of the jaw, its upper surface
being concave in front, where it passes under the articular eminence,
and thick and convex behind, where it adapts itself to the deeper por-
tion of the glenoid fossa. Its circumference affords attachment to the
common capsular ligament, while its anterior portion gives insertion to
part of the tendon of the external pterygoid muscle. Its surfaces are
smooth and divide the articulating cavity into two unequal pockets.
Sometimes an opening will be fi)und in the centre of this cartilage which
allows communication between the chambers. When this is the case
the synovial sacs are continuous with each other.
The Synovial Sacs are two pouches which secrete the fluid for
lubricating the joint. They are situated one above the other below the
interarticular disc of cartilage.
The Superior Synovial S((e is the larger and freer of the two. It
begins at the margin of the disc, and passes over the eminentia
articularis, the roof of the glenoid fossa, and the upper surface of the
cartilage.