Page 176 - My FlipBook
P. 176
172 OPERATIVE DENTISTRY
particularly that the cavo-surface angle on the incisal outline is
protected by one-half of a millimeter to a millimeter of the cast
gold. The cast should be made and set with oxyphosphate of
zinc cement. At a subsequent setting the silicate face may be built
in. A similar effect is produced with the bicuspids and molars, in
crown Avork. The gold crown is made in the usual way and set.
A carborundum stone is applied to the buccal surface and ground
away and a sufficient amount of cement cut out to make room for
the building in of the silicate. Before building in the silicate it is
best to coat the cement which is exposed within the crown with a
thin application of copal-ether varnish.
Silicate and Amalg-am. Many large contour amalgam fillings on
the mesial surfaces of bicuspids and molars particularly in the
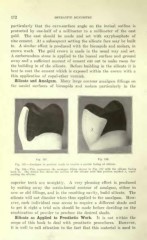
Fig. 107. Fig. 108.
Fig. 107.—Amalgam in jjosition ready to receive a partial facing of silicate.
Fig. 108.—This represents the amalgam filling shown in Fig. 107 with the silicate facing
built in. The dotted line shows the outline of the silicate with that portion marked x, repre-
senting the silicate.
superior teeth are unsightly. A very pleasing effect is produced
l)y cutting away the mesio-buccal contour of amalgam, either in
new or old fillings, and in the resulting cavity, build silicate. The
silicate will not discolor when thus applied to the amalgam. How-
ever, each individual case seems to require a different shade and
to get it right a trial mix should be made before deciding on the
combination of powder to produce the desired shade.
Silicate as Applied to Prosthetic Work. It is not within the
scope of this book to deal with prosthetic procedures. However,
it is well to call attention to the fact that this material is used to